History
We’ve long read about syphilis – the “Great Pox” – in Victorian novels. The origin of syphilis is unclear, but many believe it was first brought to Europe in the 15th century by crewmen returning from Christopher Columbus’s expedition to North America. There was no treatment before penicillin, which was not widely used to treat syphilis until the late 1940s. Before penicillin, people became disfigured, crippled and blind – and the final stage is insanity. It was not so long ago that many suffered and died from syphilis. By 1947, penicillin was the common cure.
Detection
Early detection involves noticing a painless sore at the site of infection: in the mouth, around the asshole or on the penis. Get tested immediately and do nothing to pass it on until the test results are in and you’re treated. A sore commonly appears three weeks after infection and lasts one to three weeks. Because it’s painless it can go unnoticed. But this stage is called primary syphilis, and you are highly contagious.
Transmission
HIV-negative men trying to remain that way may use condoms to fuck all the time. But most suck dick raw. Even sliding your hand between someone’s ass cheeks, then jerking yourself off with the same hand can easily transmit syphilis if that butt has it. Syphilis makes HIV look hard to catch. But it does give you options when it comes to explaining how you got it. You need only admit to sucking a syphilis lollipop.
Treatment
Treatment for syphilis varies based on HIV status and how recently infection has occurred. If you’re HIV-negative, with primary or secondary syphilis, one treatment is considered enough. For those who are HIV-positive, up to three treatments may be necessary: one every week for three weeks.
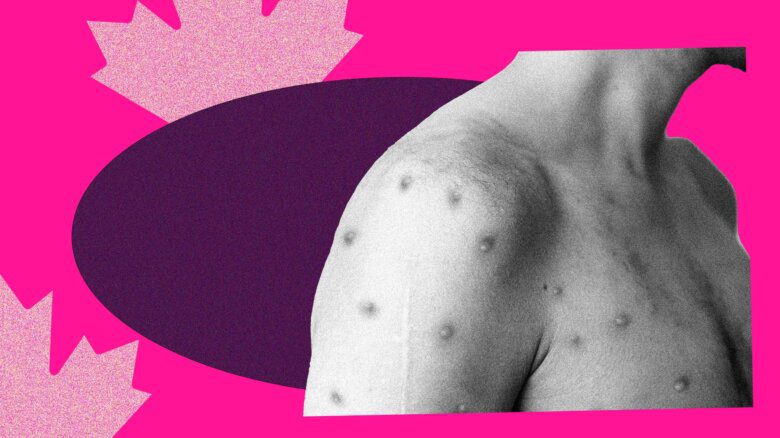
Symptoms of advanced syphilis
Common symptoms of a secondary syphilis infection may include feeling generally unwell, with fatigue, fever, achy muscles, sore throat, headache, weight loss, loss of vision and mental confusion. Hair may fall out. Lymph nodes are commonly affected. An unsightly skin rash may develop everywhere on the body, including the penis, with raw-looking blisters on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. These blisters can pass syphilis. Syphilis is called The Great Pretender because it resembles so many other infections and is often misdiagnosed. It spreads easily – orally, genitally or anally – when there is no barrier. And syphilis increases the risk of HIV transmission because of the open chancre or blisters.

 Why you can trust Xtra
Why you can trust Xtra